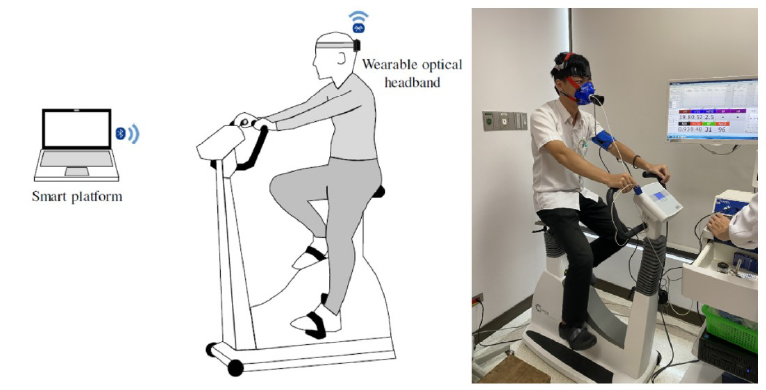
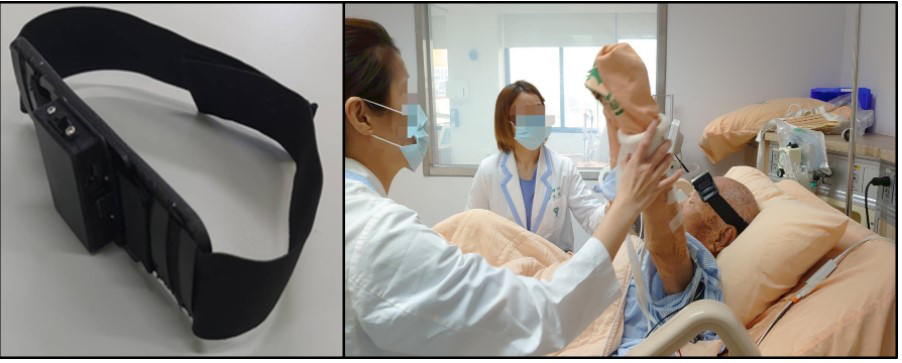
Innovative head-mounted light sensing technology calculates cerebral blood perfusion and cerebral oxygenation monitor
2021-11-17
Source:Chi-Mei Hospital
Clinically, physician prescribed different exercise training and rehabilitation procedures to improve their cardiopulmonary function (CPF) in patients with cardiovascular diseases. In previous studies, several methods have been proposed, such as cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET), cardiac ultrasound (Echocardiography) and computer tomography angiography (CTA) to indirectly assess the effects of cardiopulmonary rehabilitation effect. However, the above method requires experienced operators and complex equipment, and it is impossible to observe the activation of the brain area. Therefore, the team developed an "intelligent cerebral blood oxygenation monitor " that uses algorithms to analyze the blood perfusion state of brain tissue during incremental exercise, and uses artificial intelligence technology deep learning the hemoglobin parameter indicators to classify different cardiopulmonary diseases Therefore, it is helpful to help doctors conduct clinical evaluation on the severity of cardiovascular disease and the effect of rehabilitation on cardiopulmonary function in the future.
The intelligent cerebral blood oxygenation monitor uses biomedical photoelectric measurement technology to simultaneously monitor brain total hemoglobin concentration, cerebral blood oxygen concentration, and light absorption intensity with an optical probe, and transmit the collected physiological signals to the back-end platform by automatically analyzing the characteristics of cerebral blood flow conditions. On the hardware, the design of the head-mounted device adapts to different head contours and avoids shaking movement during rehabilitation exercises or the interference to the optical signal due to light source in the background environment. At the same time, through the trend of changes in cerebral blood flow parameters over time, several indicators related to the significance of cardiopulmonary function are defined, combined with artificial intelligence learning to assess the status of cardiopulmonary function. At present, the monitor has been used in clinical research and routine medical services, mainly in three aspects:
(1) Dementia Center for the Elderly: It is used in the exercise program of the elderly with cognitive impairments. It sets the most suitable exercise intensity for the elderly, and indicates their maximum cerebral blood flow and blood oxygen in real-time, and uses aerobic exercise training to improve their cognitive functions.
(2) Stroke Rehabilitation Center: Breaking through the traditional methods in the past, aerobic exercise training is predominated in cognitive training with this device to detect the maximum cerebral blood oxygen and cerebral blood flow to confirm the effect of exercise on the cerebral blood oxygen of the affected side in stroke patients.
(3) Delirium in the Intensive Care Unit: Confirm the correlation between delirium in the intensive care unit and cerebral blood oxygen concentration, and further use the mobility training in the early intensive care unit to improve the cerebral blood oxygen concentration, thereby improving the incidence and severity of delirium.
Non-invasive and continuous monitoring is carried out through biomedical photoelectric technology provide fast, simple, easy-to-operate, and real-time information of cerebral blood flow and blood oxygen concentration to early detect cerebral hypoxia caused by the imbalance of supply and demand in the brain; moreover, and even early prevention or management of subsequent cognitive dysfunction. It is also used for dynamic observation of blood flow changes to assess the influence of different exercise intensities on cerebral blood oxygen concentration and blood flow. Innovative cerebral blood oxygen parameters significantly related to cardiopulmonary function can assess cardiovascular disease conditions and severity via artificial intelligence technology learning.